The writing is on the wall
The red flags raised by the GHI report regarding malnutrition in India are indeed concerning, and deserve acknowledgement rather than denial
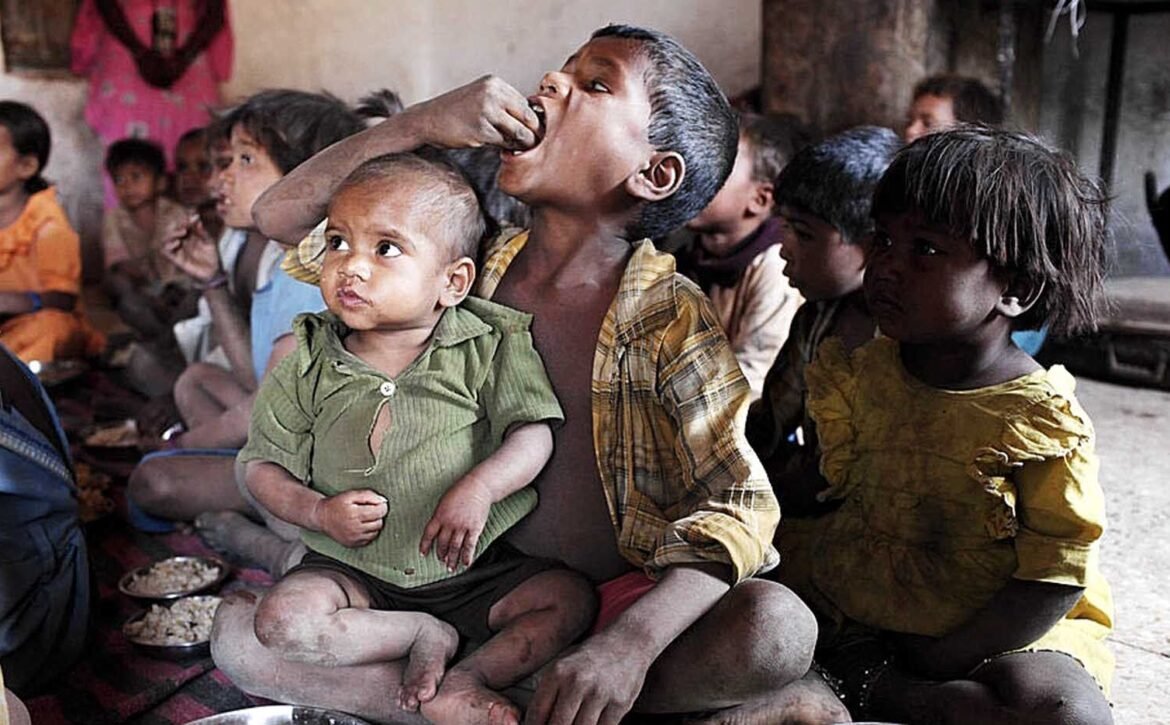
The latest global hunger index report has been released, and India has been ranked 107th out of 121 countries. This has once again stirred a controversy, with the Indian government protesting and responding by summarily rejecting the report and claiming that this is a part of a consistent effort to taint India’s image. The global hunger index gives the impression that it is about shortage of food and a large number of people going hungry. This is definitely not the state of affairs in India where we have achieved food security, and there is no one who is remaining hungry for want of food. However, the GHI is a multidimensional index of hunger, which makes it much more complex. Its four measures are child mortality under five years, child wasting, child stunting and under nourishment. These measures have been used ever since the inception of this index in 2006. It is not as if some new measures have been used to obtain the current ranking.
The Indian side argues that this analysis is based on inadequate data. Proper data regarding these measures is often not properly computed or presented by various states of the country and, as such, the GHI relies upon some kind of an approximation or projection of incomplete data. It has also been argued that in order to calculate the index, the GHI has been selective and discretionary in terms of using the data. Essentially, the issue is about unreliable data being used. In a similar vein, India reacted to its low score in the human development index (HDI) as well. It alleged that data regarding the deaths during the pandemic, where excess death figures were used to calculate life expectancy, were incorrect. However, GHI or HDI are not India-specific surveys. The GHI website has clearly stated that its findings are based on data officially reported by the member countries, including India.
The GHI report should come as a shock to us when we realise the extent of malnourishment prevailing among children in our country. Reacting to similar findings in 2012, the then Prime Minister Manmohan Singh had acknowledged that such a high level of malnutrition was a matter of national shame. The GHI index considers child mortality as the percentage of children who die before reaching the age of five, due to inadequate nutrition or disease. Data show that India has 3.3 per cent under-five mortality rate, which is higher than Bangladesh at 2.9 per cent, Indonesia at 2.3 per cent and China at 0.7 per cent. Of course, we are better than Pakistan which is at 6.5 per cent.
The second indicator considered by the GHI is the proportion of people who are undernourished in the population. India fares quite poorly at 16.3 per cent, which is much higher than Bangladesh at 11.4 whereas China is less than 2.5 per cent. Similarly, India performs badly along the indicators of stunting and wasting of children of less than five years age. As many as 35.5 per cent of children in India are suffering from stunting (children under five who have low height for their age, resulting from undernourishment), which is extremely high. This indicator accounts for 1/6th of the GHI score. Similarly, 19.3 per cent of under-five Indian children suffer from wasting, which is much higher than the figure of 9.8 per cent for Bangladesh and 1.9 per cent for China. Even Pakistan scores better at 6.5 per cent. The weightage assigned to wasting is 1/6th of GHI score. The overall score is 100, and the lower a country scores the better its performance.
The Government of India has rightly pointed out that three out of these four variables relate to children and, hence, cannot be taken as an indicator of the entire population. There is merit in this argument but it is also true that India is facing a crisis of undernourishment, particularly among children, which is indeed a matter of great concern for policymakers. The government has started a Poshan (nourishment) Abhiyan but a lot of work still needs to be done. States like Uttar Pradesh and Bihar are particularly vulnerable. We have to take urgent steps to eradicate malnutrition among children, which would need maintaining real-time data of the weight and height of children and targeting government schemes to take them out of this sorry state of affairs. Rather than spending time on finding ways of being critical of the GHI, the Central and state governments must accord the highest priority to this issue. Lately, another international report has come, which shows that between 2004-05 and 2019-20, India was able to take 41 crore people out of poverty, which is a major achievement, and shows that with the right kind of leadership and political will, it is possible to free the children of our country from the scourge of stunting and wasting.
The infant mortality figures indicate that a lot needs to be done to improve healthcare facilities, especially in the rural areas. We are spending only 1.2 per cent of our GDP on healthcare, which has to be raised to 2.5 per cent at the earliest. Moreover, healthcare has to be attended to in a holistic manner by synergizing between the schemes related to health, nutrition, water, sanitation and education.
We may concede that the term GHI does give rise to an erroneous perception about hunger. It would be better if this indicator could be called the global nutrition index. But then, as it is said, what’s in a name? The stark reality is before us and denial is not the right response. The problem of under-nourishment has to be understood, accepted and a frontal attack needs to be launched to free the country of this menace.
The writer is an ex-Chief Secretary, Govt of Uttar Pradesh. Views expressed are personal